Adobe Photoshop Training by Experts
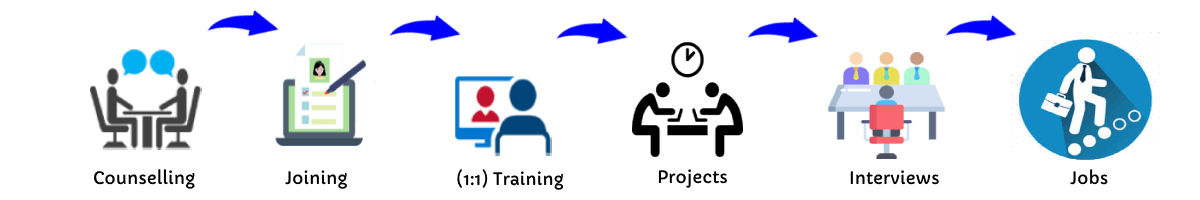
Our Training Process
Adobe Photoshop - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
- Overview of Photoshop and its applications
- Introduction to the workspace:
- Toolbar, options bar, panels, and canvas
- Setting up a new document and file formats
- Basic navigation: Zoom, pan, and rotate view
- Saving and exporting projects
- Understanding layers and the Layers panel
- Layer types: Text, adjustment, and shape layers
- Using selection tools:
- Marquee, Lasso, and Quick Selection tools
- Refine Edge and Select Subject
- Basic masking techniques
- Adjusting brightness, contrast, and levels
- Color corrections: Hue/Saturation and Color Balance
- Using Adjustment Layers for non-destructive editing
- Introduction to filters and smart filters
- Sharpening and blurring images
- Healing Brush, Spot Healing Brush, and Patch tools
- Clone Stamp tool
- Content-Aware Fill and Move
- Removing unwanted objects from images
- Basic portrait retouching techniques
- Adding text and using the Type tool
- Formatting text: Fonts, sizes, and styles
- Working with paragraph and character panels Applying text effects: Drop shadows, strokes, and gradients
- Typographic layouts and text on paths
- Introduction to the Pen Tool for paths and shapes
- Applying layer styles and blending modes
- Using gradients and patterns
- Introduction to brushes and custom brushes
- Creating basic photo manipulations
- Planning and executing a creative project
- Reviewing core tools and concepts
- Tips and best practices for Photoshop workflows
- Feedback on student projects
Module 1: Introduction to Photoshop (2 Hours)
Objective: Understand the basics of Photoshop, its interface, and core tools.
Practical: Create and save a simple document with basic shapes.
Module 2: Working with Layers and Selections (2 Hours)
Objective: Master layers, layer properties, and selection tools.
Practical: Create a composition using multiple images and adjust layer opacity.
Module 3: Image Adjustments and Enhancements (3 Hours)
Objective: Learn to enhance photos using adjustments and filters.
Practical: Enhance a photograph by correcting color and applying filters.
Module 4: Retouching and Repairing Images (2 Hours)
Objective: Use retouching tools for professional image editing.
Practical: Remove blemishes and unwanted objects from a provided image.
Module 5: Text and Typography (2 Hours)
Objective: Add and manipulate text for graphic design purposes.
Practical: Create a poster with creative text effects.
Module 6: Creative Tools and Special Effects (2 Hours)
Objective: Explore creative possibilities with Photoshop tools and techniques.
Practical: Design a surreal photo manipulation using multiple tools.
Module 7: Final Project and Review (2 Hours)
Objective: Consolidate learning by applying all techniques in a final project.
Practical: Complete a final project (e.g., a social media post, flyer, or edited photo).
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 Photoshop creates an artist's virtual studio/darkroom. If you're employed in the graphics field, getting to understand Adobe Photoshop could be a prerequisite. Photoshop includes a selection of quality tools and is well customizable to suit your work style. Also, it has wide job opportunities within the middle east. after completion of the course, if you have any doubt regarding it our team is often with you. Most graphic designers use photoshop for their skilled work because photoshop is one of the foremost skilled editing codes available nowadays. With courses and coaching from Nestsoft, you may research the skills to become a Photoshop expert. . Image editors and website creators widely use it. Your works on the projects build it easier and add more by adding special effects or fascinating options on plugins and you'll use numerous tools like brushes, overlays, fonts, textures etc.
Photoshop creates an artist's virtual studio/darkroom. If you're employed in the graphics field, getting to understand Adobe Photoshop could be a prerequisite. Photoshop includes a selection of quality tools and is well customizable to suit your work style. Also, it has wide job opportunities within the middle east. after completion of the course, if you have any doubt regarding it our team is often with you. Most graphic designers use photoshop for their skilled work because photoshop is one of the foremost skilled editing codes available nowadays. With courses and coaching from Nestsoft, you may research the skills to become a Photoshop expert. . Image editors and website creators widely use it. Your works on the projects build it easier and add more by adding special effects or fascinating options on plugins and you'll use numerous tools like brushes, overlays, fonts, textures etc.