Software Testing Training by Experts
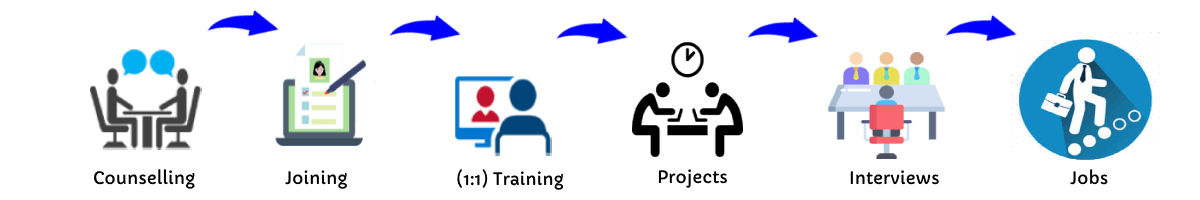
Our Training Process
Software Testing - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Automation Testing Syllabus
- Sql introduction
- Sql Datatypes Sql basics-DDL
- DML,DCL,Comparison Operators
- Constraints
- Aggregate
- Functions
- Practice questions
- Joins
- Stored Procedures
- Practice Question
- Views
- Group By
- Having
- Order By Clauses Practice Question
- Introduction to the course
- Java Installation
- Features and JDK
- First Sample Program Data Types and Variables
- Operators Control Statements
- Loops Scanner
- Array Oops - Polymophism (Method overloading)
- Constructor Overloading
- Types of Inheritance and Method Overriding
- This and Super keyword
- final and static keyword
- Abstraction, Encapsulation, Exception, Thread
- Thread Synchronization
- Events Collection - List & Set Collection - Map & Queue Exam - Java
- Selenium Introduction
- IDE Features
- creating script Using IDE
- Recording
- Selenese
- Assert and verify Export Testcase
- Selenium Webdriver Introduction
- Webdriver manager
- Junit
- Locators
- Screenshot in selenium
- Handling Alerts
- BrokenLinks
- Testng and its Features
- Waits in Selenium
- Javascript Executor in Selenium
- Navigation Commands
- Dropdown handling using select class
- Button Text verification
- Radio buttons Actions class
- copy paste using action class
- draganddrop program Double click and right click using Action class
- Mouse Hover Program
- File upload
- File upload using AUTO IT and Robot class
- Cross browser Testing
- Handling multiple windows and tabs
- Handle pops in Chrome
- Datepicker
- DataDrivenTesting
- Extended Reports
- POM Design Pattern Frameworks
- Datadriven framework Maven
- Importance of maven
- Create Project in Maven
- Project
- Introduction to Jmeter
- overview of performance testing
- Jmeter workflow
- components of Jmeter
- Building a web Test plan
- Report generation
- Execution in NON-GUI mode Recording in Jmeter
- Blaze meter plugin Assertions
- Timers
- CSV Data set configuration
- Correlation
- Introduction to Postman
- API testing
- Download and install postman
- Collections
- Request methods
- Collection Runner
- Test script
- Variables
- Data driven testing
- API fetching
- JsonPathfinder
- Openweathermap API
- Newman
- Agile methodology
- scrum
- Introduction to Jira
- Jira issue types
- How to create an Epic/User stories in Jira
- Creating sprints in Jira
- Sprint lifecylce in Jira
- Backlogs
- Creating bugs
- Write Test Cases in Jira with Zephyr plugin
- Jira project flow
- Introduction
- Git installation
- Repository creation in GitHub
- Commands in git
MODULE 1 - SQL
MODULE 2 - JAVA
MODULE 3 - Selenium IDE
MODULE 4 - Selenium Webdriver
MODULE 5 - JMeter
MODULE 6 - POSTMAN
MODULE 7 - JIRA
MODULE 8 - GIR & GITH
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates
Manual Testing Syllabus
- What is Software testing?
- Importance of Software testing
- Basic terminology of Software testing
- Difference between Manual and Automated Testing
- Software testingPrinciples
- Levels of Testing
- Software development life cycle
- Requirements phase
- Analysis phase
- Design phase
- Coding phase
- Testing phase
- Release and maintenance phase
- Software Development life cycle models
- Waterfall model
- Agile model
- Spiral model
- V model
- Software Testing Life Cycle
- Testing Constraints
- Static Test Design
- Formal review
- Informal reviews
- Walkthroughs
- Technical review
- Inspection
- Dynamic test design
- White-box testing
- White-box testing technique
- Black box testing
- Black box testing technique
- Grey box testing
- Test plan document
- Scope of document
- Objective of testing
- Customisation of Test Plan document
- Requirement Traceability Matrix
- Importance of Test case
- Test case template
- Test Scenario
- Test Strategy
- Functional Testing Types
- Sanity Testing
- Smoke Testing
- Retesting
- Regression testing
- Adhoc testing and types
- UI testing
- Positive Testing
- Negative Testing
- Alpha and Beta Testing
- Non-functional Testing
- Performance testing
- Load testing
- Stress Testing
- Volume Testing
- Security testing
- Portability testing
- What is a bug?
- Bug life cycle
- Severity
- Priority
- Types of Bugs
- Bug Report Template
- Metric types and calculation
- Test Report Template
MODULE 1 - Introduction to Manual Testing
MODULE 2 – SDLC and STLC
MODULE 3 – Static and Dynamic Testing
MODULE 4 – Test Plan and Test Case Documents
MODULE 5 – Types of Testing
MODULE 6 – Bug Report and Test Report Documents
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 Manual testing enables human observation, which may be more effective for detecting potential flaws in dynamically charging GUI designs and usability testing. The certificate is only given out after our course has been completed successfully. It boosts the worth of your resume. Selenium, lambda test, test complete, test project, katalon studio, Avo ensure, cross-browser testing, appium, Hobbiton, TestNG, and others are examples of automation tools used. The software testing automation field has become the fastest expanding industry in terms of commercial IT spending, thus there are several prospects in this Toowoomba.
Automation testing is a software testing method in which the actual result is compared to the predicted outcome. Beginners, intermediates, and specialists can use the software testing automation. They have over 15 years of real-world software testing expertise and are certified QA consultants. Learning and adopting new technology is driving the expansion of automated testing training from Toowoomba. There is no need for human intervention.
Manual testing enables human observation, which may be more effective for detecting potential flaws in dynamically charging GUI designs and usability testing. The certificate is only given out after our course has been completed successfully. It boosts the worth of your resume. Selenium, lambda test, test complete, test project, katalon studio, Avo ensure, cross-browser testing, appium, Hobbiton, TestNG, and others are examples of automation tools used. The software testing automation field has become the fastest expanding industry in terms of commercial IT spending, thus there are several prospects in this Toowoomba.
Automation testing is a software testing method in which the actual result is compared to the predicted outcome. Beginners, intermediates, and specialists can use the software testing automation. They have over 15 years of real-world software testing expertise and are certified QA consultants. Learning and adopting new technology is driving the expansion of automated testing training from Toowoomba. There is no need for human intervention.