Wordpress Training by Experts
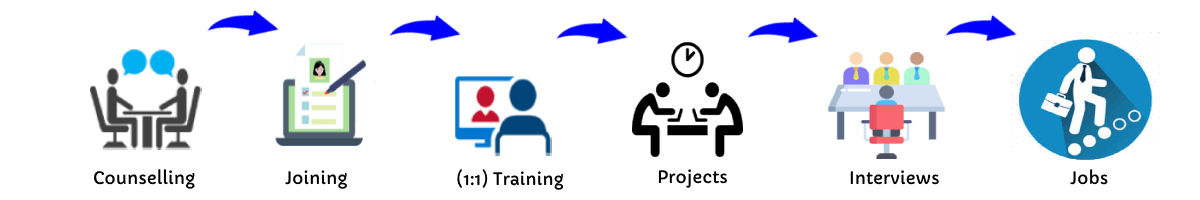
Our Training Process
Wordpress - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
- Wordpress Installation
- Domain Name Registration & Web Hosting
- Understanding FTP
- Wordpress Admin/Settings/Dashboard
- Wordpress Toolbar
- Why CMS (Content Management System)
- Managing Posts, Pages and Blogs
- Using Page Templates
- Visual Editor, Formatting, Hyperlinks etc.
- Using Wordpress for Website Development
- Manage Users (Adding & Managing)
- Installation Social Media Plugins
- Installation Form Plugins
- Installation Woocommerce / E-commerce Plugin
- Managing Media: Image Gallery, Video & Multimedia
- Manage Categories, Tags and Menu Links
- Discussion Settings
- Themes & Widgets (Installing, Appearance and Activating)
- Customize Logo, Title, & Tagline
- Customize Header, Colors, Layout
- Customize Wordpress for Mobile (Responsive)
- Adding a Site Icon (Favicon)
- Installing & Manage Wordpress Plugins
- Wordpress Database (DBManager)
- Yoast SEO (Wordpress SEO)
- Upgrading / Updating Wordpress
- Security Plugins
- Automated Backups
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 After completion of the course, if you have any doubt in this field we always help you. Plugins make your website professional and each plugin has its own role. WordPress could be a content management system that powers many of the most common sites on the web. Our expert trainers help you with the creation of content, managing, and handling of WordPress Plugins. Our WordPress classes are taken from basic level to Advanced Level, handled by experts in this field. It permits it to run, lets you edit the content of the site, produces new posts and pages, and then makes assure that your website displays properly on all devices. If you’re not considering launching a completely featured site yet, however just need to experiment with WordPress, you would possibly need to think to consider contemplating WordPress on a local server. WordPress is easy to use for even people who are from non-technical backgrounds. Do you need to learn the WordPress concepts in an easy manner?. It doesn't need more coding knowledge so it is very simple to build a website.
After completion of the course, if you have any doubt in this field we always help you. Plugins make your website professional and each plugin has its own role. WordPress could be a content management system that powers many of the most common sites on the web. Our expert trainers help you with the creation of content, managing, and handling of WordPress Plugins. Our WordPress classes are taken from basic level to Advanced Level, handled by experts in this field. It permits it to run, lets you edit the content of the site, produces new posts and pages, and then makes assure that your website displays properly on all devices. If you’re not considering launching a completely featured site yet, however just need to experiment with WordPress, you would possibly need to think to consider contemplating WordPress on a local server. WordPress is easy to use for even people who are from non-technical backgrounds. Do you need to learn the WordPress concepts in an easy manner?. It doesn't need more coding knowledge so it is very simple to build a website.