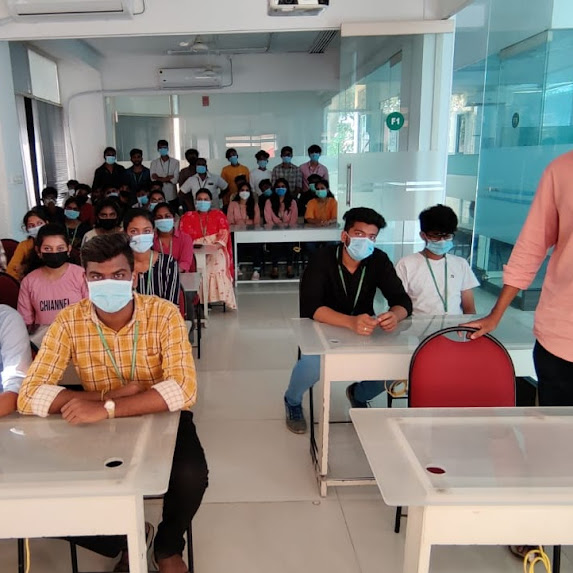
Fortinet Firewall Training by Experts
Our Training Process
Fortinet Firewall - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
MODULE 1
- System setup
- Fort guard subscription services
- Logging
- Firewall policies
- Policies
- Policies lab
MODULE 2
- Firewall
- Firewall types
- How to control access
- Managing firewall
- NAT
- Denial of service (DoS)
MODULE 3
- Basic VPN
- VPN uses, advantages and types
- Need of firewall in VPN
- Threat free tunneling
- VPN Bandwidth management
- SSL VPN
- SSL VPN with RADIUS and forti token
- SSL VPN using web and tunnel mode
- Dialup IPsec VPN
MODULE 4
- Authentication
- Requirement and types of authentication
- Group authentication
- Traffic discovery
- AD, LD AP, OR RADIUS
MODULE 5
- Antivirus
- Functioning of Anti-Virus & Anti-Spam
- Basics of Virus, Spyware, Malware, Phishing, and Pharming.
- Web/Mail/FTP Anti-Virus
- Gateway level Anti-Virus/Anti-Spam
- Instant Messaging
- Virus Outbreak Detection
- Recurrent Pattern Detection
- RBL, IP Reputation
- Understanding of Intrusion
- Signature-based detection
- Statistical anomaly-based detection
- Stately protocol analysis detection
- Network-Based IPS & Wireless Based IPS
- Network Behaviour Analysis
- Host-Based IPS
MODULE 6
- Spam filtering
- Web filtering
- Need for web filtering
- Web 2.0 filtering
- Filtering with keywords, URL
- Filtering web traffics
MODULE 7
- Application firewall
- Evolution of Application Firewall
- File Filtering
- Application & P2P Filtering
- Instant Messaging Filters
- Custom Filters
- Compliance based filtering
MODULE 8
- WiFi
- Wifi settings
- Wifi MAC filter
- Wifi monitoring
MODULE 9
- Network availability
- High availability
- Load balancing
- Understand balancing
- Multilink manager
- Active-Active load balancing and gateway failover
- Active – Passive configuration and gateway failover
- MPLS failover to VPN
- Automatic ISP failover detection
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 For administration, use the GUI and CLI. Rather than being borderless, networks have become porous, with unprecedented numbers of points of access and endpoints.
Small and medium-sized businesses, as well as major firms, data processicentersres, and Internet providers, can benefit from Fortigate's extensive offerings.
Understand the responsibilities of encryption and certificates. The Fortinet Toowoomba course is a basic platform tailored toward various types of enterprises. And, as malware and threats grow more difficult to detect at the access point, security must be extended across the network to monitor behaviors and reveal intent.
This course gives students from all over the world industry-recognized Fortinet training and certification options, allowing them to join an exclusive group of cybersecurity professionals.
After completing the course from Toowoomba you should be able to: Implement the right mode of operation for your network after completing this course.
NESTSOFT train IT and Fortinet ecosystem workers in information, configuration, and management to safeguard networks of enterprises whose most valuable asset is their data. According to the latest Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) report, SSL was employed by 75% of all phishing sites in the first quarter of 2020.
For administration, use the GUI and CLI. Rather than being borderless, networks have become porous, with unprecedented numbers of points of access and endpoints.
Small and medium-sized businesses, as well as major firms, data processicentersres, and Internet providers, can benefit from Fortigate's extensive offerings.
Understand the responsibilities of encryption and certificates. The Fortinet Toowoomba course is a basic platform tailored toward various types of enterprises. And, as malware and threats grow more difficult to detect at the access point, security must be extended across the network to monitor behaviors and reveal intent.
This course gives students from all over the world industry-recognized Fortinet training and certification options, allowing them to join an exclusive group of cybersecurity professionals.
After completing the course from Toowoomba you should be able to: Implement the right mode of operation for your network after completing this course.
NESTSOFT train IT and Fortinet ecosystem workers in information, configuration, and management to safeguard networks of enterprises whose most valuable asset is their data. According to the latest Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) report, SSL was employed by 75% of all phishing sites in the first quarter of 2020.