AutoCAD Training by Experts
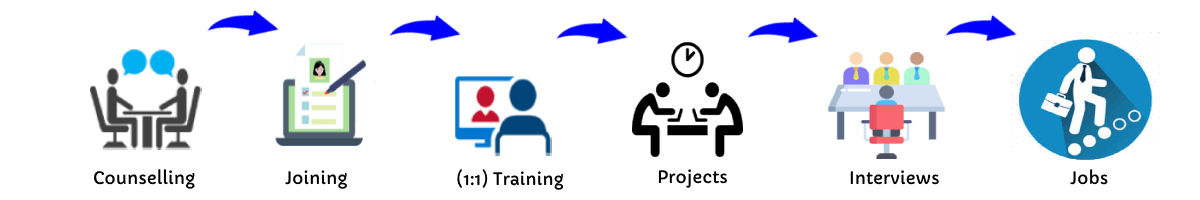
Our Training Process
AutoCAD - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
INTRODUCTION OF AUTOCAD
- Uses of AutoCAD
- Different versions
- Installation procedure
BASIC UNDERSTANDING
- User interface
- Different units and templates
- Coordinate systems
- Drawing settings
- Concept of views
- Create and Save
BASIC IDEA OF TOOLS AND MENUS
- Application button
- Quick access toolbar
- Tabs and ribbon areas
- Panels
- Drawing area
- Status bar
BASIC DRAWINGS
- Making simple lines, polylines, rectangles
- Creation of arcs, circles, ellipses
- Use of ortho and polar mode
- Simple and advance object snaps
- Object snap tracking
BASIC MODIFY TOOLS
- Scaling of objects
- Rotation of objects
- Move, copy ,trim and extend objects
- Joining and extend tools
- Offset, fillet and mirror of objects
MAJOR DRAWINGS
- Isometric, mechanical and electrical drawings with advanced building drawings
- Drawing with Hatch tools and their applications
- Making rectangular, polar and path array
- Use of multi function grips and dynamic input
- Drawing of different components of building
REUSING EXISTING CONTENT
- Creation, understanding and insertion of blocks
- Modifying and start write block
- Use of different block libraries
- Attributes
OBJECT ORGANISATION
- Understanding and assigning layers
- By layer and by block
- Enquiry tools
- Purge and rename command
ANNOTATIONS
- Basic and advance dimensions and their style
- Multileader
- Creation and modifying table with styles
- Different text styles
LAYOUT AND PRINTING
- Page setup and plotting drawing
- Viewports
- Creation of annotative dimensions
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 It is developed and marketed by Autodesk. But now it can be used for various purposes. They are also adopted as a skill development application for a graduate-level of education. AutoCAD is a commercial designing and drafting software application in Toowoomba. Initially AutoCAD was derived from a program called Interact, which was written in a proprietary language. It has evolved to become one of the most sophisticated design tools in the industry these days. The designed blueprint will be carried with the job for its complete stages of start to delivery in between production teams, quality team and machine handling teams review the design in case of any issues of understanding and continue machining with the reference of blueprint drafters. Its first release only use entities such as polygons, circles, lines, arcs, and text to construct complex objects.
AutoCAD training by TechnoMaster in Toowoomba by Industry Experts. In electrical engineering, it is used to map out electrical systems, and in civil engineering, it is used to design bridges and roads.
It is developed and marketed by Autodesk. But now it can be used for various purposes. They are also adopted as a skill development application for a graduate-level of education. AutoCAD is a commercial designing and drafting software application in Toowoomba. Initially AutoCAD was derived from a program called Interact, which was written in a proprietary language. It has evolved to become one of the most sophisticated design tools in the industry these days. The designed blueprint will be carried with the job for its complete stages of start to delivery in between production teams, quality team and machine handling teams review the design in case of any issues of understanding and continue machining with the reference of blueprint drafters. Its first release only use entities such as polygons, circles, lines, arcs, and text to construct complex objects.
AutoCAD training by TechnoMaster in Toowoomba by Industry Experts. In electrical engineering, it is used to map out electrical systems, and in civil engineering, it is used to design bridges and roads.