Autodesk Maya Training by Experts
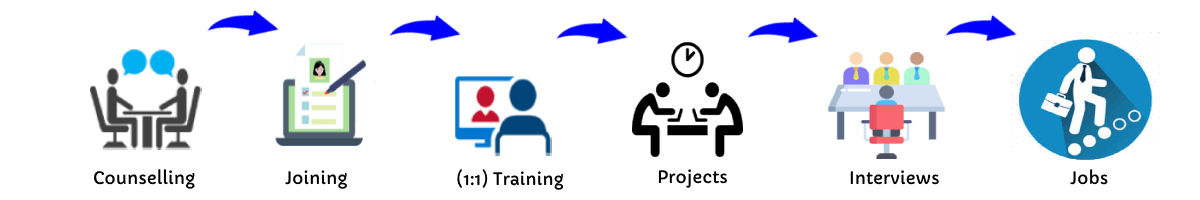
Our Training Process
Autodesk Maya - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Overview of Maya
- Understanding the Maya interface
- Setting up files and Maya projects
- Configuring viewports
- Customizing the interface
- Navigating the Maya workspace
- Using the hotbox and marking menus
- Selecting objects
- Using the Move tool
- Rotating and scaling objects
- Working with pivots
- Understanding the Channel Box
- The Attribute Editor
Maya Scenes
- Organizing Maya Scenes
- Working with the Outliner
- Dealing with hierarchies
- Object groups
- Exploring Hypergraph
- Hiding and showing objects
- Working with layers
- Working with selection masks
Working with Polygons
- Creating Polygonal Models
- Differences between NURBS and polys
- Selecting polygonal components
- Using Soft Select and reflection
- Sculpting with the Sculpt tool
- The Combine and Separate commands
- Working with subdivision surfaces
Working with Meshes
- Working with edge loops
- Using Edge Flow for smooth geometry
- Reorienting geometry using Spin Edge
- Drawing detail with the Connect tool
- Mirroring geometry
- Modeling with nonlinear deformers
- Modeling with lattices
NURBS-based Modelling
- Refining NURBS Models
- Extracting NURBS curves from surfaces
- Open/ Close curves and surfaces
- Creating curves on a surface
- Projecting curves on surfaces
- Trimming NURBS surfaces
- Using fillets to connect surfaces
- Converting NURBS to polygons
Using Materials
- Creating Materials
- Overview of Maya renderers
- The basics of materials
- Creating and applying maps
- Using bitmaps as texture
- Working with the Hype shade window
- Using the Ramp material
- Displacement and bump maps
- Mental ray materials
Using Textures
- Applying Textures
- Texture mapping
- Projecting textures on surfaces
- Applying multiple materials
- UV mapping
- The UV Texture Editor
Rendering your Scene
- Render Settings
- Lights and lighting types
- Rendering shadows
- Camera basics
- Depth of field
- Motion Blur
- Reflections and refractions
- Matching lights and shadows to images
- Batch rendering
Animating in Maya
- The animation interface
- Set Key
- The Graph Editor
- The Dope Sheet
- Animating objects along spline paths
- Ghosting animation
- Animation playback using Playblast
- Creating animation cycles
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 they are even culpable for writing the program content which can be a mixture of absolute diligence and their promoting expertise. Trainees will get to search out excuses for all the ideas from basics to advanced level. it is the integration with alternative Autodesk software systems like motion builder and Mudbox. within the history of computer graphics, Maya is the most widespread 3D animation and modeling program. Meet Maya from Autodesk. Maya software is widely used so probably everybody with eyes has been exposed to one factor designed with Maya software. whether or not you’re wanting to begin a new career within the 3D animation industry, or incorporate 3D animations into your existing work for broadcast or the web. The options of Maya aren't like using only modifiers, you'll be able to apply modeling layers but it is a free-form approach to 3D modeling. It will do plenty of things, however, it’s generally accepted that it's best at animation.
.
they are even culpable for writing the program content which can be a mixture of absolute diligence and their promoting expertise. Trainees will get to search out excuses for all the ideas from basics to advanced level. it is the integration with alternative Autodesk software systems like motion builder and Mudbox. within the history of computer graphics, Maya is the most widespread 3D animation and modeling program. Meet Maya from Autodesk. Maya software is widely used so probably everybody with eyes has been exposed to one factor designed with Maya software. whether or not you’re wanting to begin a new career within the 3D animation industry, or incorporate 3D animations into your existing work for broadcast or the web. The options of Maya aren't like using only modifiers, you'll be able to apply modeling layers but it is a free-form approach to 3D modeling. It will do plenty of things, however, it’s generally accepted that it's best at animation.
.