CSS Training by Experts
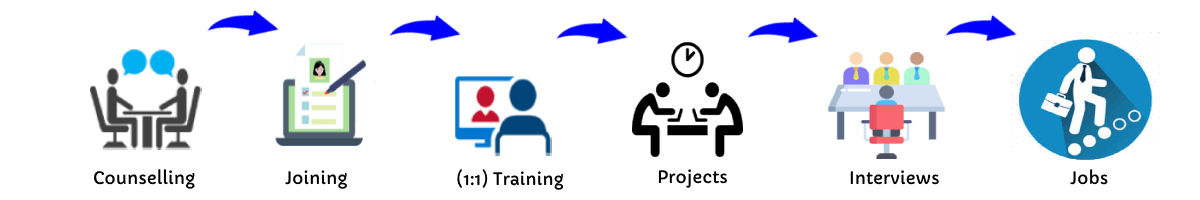
Our Training Process
CSS - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Introduction
- HTML structure and content
- Advantages of CSS
- Creating and using style sheets
- CSS Rules: The Basic Syntax
CSS Boxes and CSS Selectors
- The CSS box model
- CSS and logical HTML structure
- Styling boxes, borders, margins, and padding
- Using IE6 standards mode
- Sh4ecifying CSS distances
- and many other CSS techniques
Fonts and Text
- Using custom fonts
- Font properties
- Web font formats
- Type Kit, font squirrel
Text Formatting in CSS
- Fundamentals of text formatting
- Typefaces, alternatives, and defaults
- Font characteristics
- Formatting blocks of text
- Using arbitrary inline tags
CSS Selectors and Selections
- Using HTML element IDs in CSS
- Using CSS descendant selectors
- Descendant selector examples
- Child, sibling, and pseudo-class selectors
- And many other CSS techniques.
CSS positioning
- Choosing the right CSS
- Technique for positioning blocks
- The position property, floats, and margins
- Static positioning and normal flow
- Absolute positioning outside normal flow
- Fixed positioning outside normal flow
CSS page Layout
- Alternative methods of CSS positioning
- Styling lists
- Redefining the behaviour of inline and block elements
- Table formatting in CSS
- Styling table cell borders
- page layout with table dish4lay properties
Cascade, precedence, Specificity, and Inheritance in CSS
- Cascading and cascade order
- Resolving style conflicts by Origin & Importance
- Resolving style conflicts by Specificity & Order
CSS Layers and Translucency
- Different forms of layered presentations in CSS
- Layering with the z-index property
- Different methods for creating translucency effects
- The CSS3 opacity property
Using CSS in the Real World
- Deploying CSS
- CSS formatting vs. HTML formatting
- Standard tags and semantic markup
- Screen size and fluid design
- Table layout and CSS positioning
- Cross-platform testing
Useful CSS Tips
- Usage of CSS Sprites
- Pseudo Selectors
- CSS Minify
- Cheat Sheet for CSS3
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 completing this CSS coaching at Nessoft, you can step ahead in your career as a designer and build the newest interactive pages for your website viewers. thus entire website's look will change by editing one style sheet therefore one style sheet ensures that your websites have consistent styling throughout your website. If you would like to alter the content you simply have to edit one style sheet, because an external style sheet will contain all the designs for your website. Actually, CSS does not would like more time and stress to develop a website due to its speed and simple maintenance. . The developer will write and edit CSS codes by using CSS text editor software. CSS3 is the latest in styling standards and can modify you to bring many new properties and declarations to create your website design more easily created. CSS is used to style hypertext markup language code through that you will build enticing websites therefore we will say CSS plugs directly into your HTML, even the most recent HTML5 standards. Nestsoft provides the most effective CSS coaching style for a web page and building CSS classes from a beginner level to a professional level. Our training on CSS and CSS3 offers the most effective coaching in cascading style sheets (CSS) the most coding files used to layout a website and its design.
completing this CSS coaching at Nessoft, you can step ahead in your career as a designer and build the newest interactive pages for your website viewers. thus entire website's look will change by editing one style sheet therefore one style sheet ensures that your websites have consistent styling throughout your website. If you would like to alter the content you simply have to edit one style sheet, because an external style sheet will contain all the designs for your website. Actually, CSS does not would like more time and stress to develop a website due to its speed and simple maintenance. . The developer will write and edit CSS codes by using CSS text editor software. CSS3 is the latest in styling standards and can modify you to bring many new properties and declarations to create your website design more easily created. CSS is used to style hypertext markup language code through that you will build enticing websites therefore we will say CSS plugs directly into your HTML, even the most recent HTML5 standards. Nestsoft provides the most effective CSS coaching style for a web page and building CSS classes from a beginner level to a professional level. Our training on CSS and CSS3 offers the most effective coaching in cascading style sheets (CSS) the most coding files used to layout a website and its design.