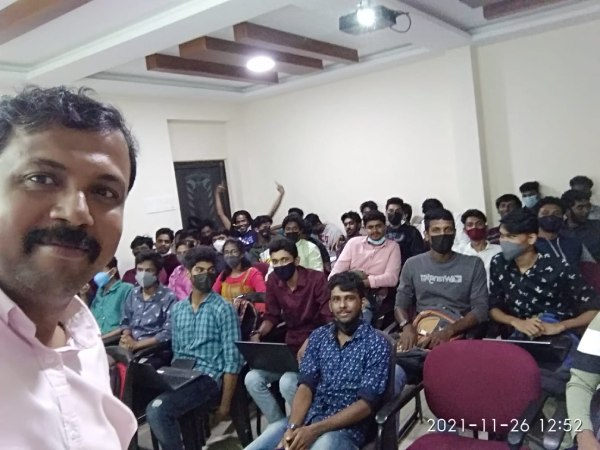
Node JS Training by Experts
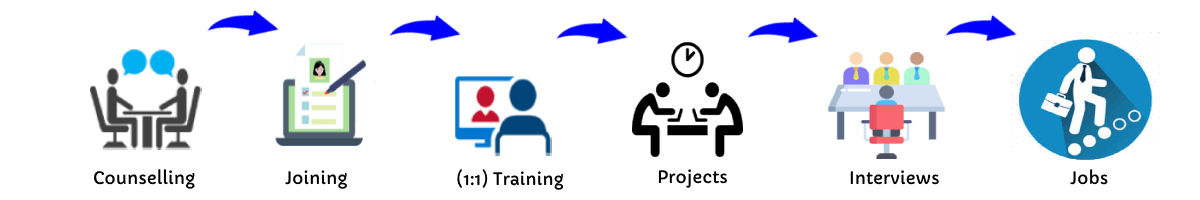
Our Training Process
Node JS - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Module 1: Introduction to Node.js
- What is Node.js
- Features of Node.js
- Concept
- Where to fit and not fit
- Event-Driven programming style
- What is Asynchronous
Module 2: Installation / Setup
- Local environment setup
- Node.js runtime
- Download source code
- Installation on OS
- Verify
Module 3: Node Package Manager
- Install module by NPM
- Global vs Local setup
- Update Module
- CRUD Module
Module 4: Express Framework
- What is Express
- Setup Express
- Request And Response
- Handling Routes
- Route Middleware
- Objects
- Cookies Management
- File upload
- HTTP methods
Module 5: Buffers and Streams
- What is buffers and Streams
- Benefit of Streams over buffers
- Create / Write / Read operation on Buffers
- Process on Buffers
- Read / Write data by Streams
- Pipeline
- Chaining Stream
Module 7: REST API
- RESTful Architecture
- HTTP URI and Methods
- RESTful web services
- Expose solution as API
- Best practice for REST API solution
Module 8: Callback
- What is Callback
- Benefit of Callback
- Asynchronous communications
- Block and Non-Blocking
- Standard Callback pattern
- Async Flow control Library
- Executing in parallel
Module 9: Events
- What is Events
- Events types
- Event Emitter API
- Multiple event listeners
- Event emitter pattern
- Class methods
- Event Loop
- Blocking Event Loop
- Escaping Event Loop
Module 10: Connecting with Database
- Introduction of MySQL
- Connect with MySQL
- Introduction of MongoDB
- Features of MongoDB
- Connect with MongoDB
- Defining a schema
- Defining a Model
Module 11: External Processes and Services
- What is processes
- Spawning Child process
- Create and kill processes
- Building with HTTP Severs
- HTTP requests
- Secure HTTP Server
Module 12: External Processes and Services
- Using Test Runner
- Using Assertion Testing Module
- Built-in Debugger
- Console log
- Node Inspector
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 . you'll learn how to create applications backed by MongoDB and gain in-depth knowledge of REST architecture, implement testing, build applications the usage of microservices design, and write a real-time chat software using Socket IO. Node. The coaching costs for developers are usually high, but when it comes to Node. Node. Node Package Manager (NPM) is one of the world’s prime package registries. so the fundamental syntax and specifications are of JavaScript only. It permits them to develop light and fast systems with spectacular real-time responses that may be scaled up as time goes on, and have further modules added on to the present ones. Node. js services are becoming more popular, in order that they need one thing new all the time.
. you'll learn how to create applications backed by MongoDB and gain in-depth knowledge of REST architecture, implement testing, build applications the usage of microservices design, and write a real-time chat software using Socket IO. Node. The coaching costs for developers are usually high, but when it comes to Node. Node. Node Package Manager (NPM) is one of the world’s prime package registries. so the fundamental syntax and specifications are of JavaScript only. It permits them to develop light and fast systems with spectacular real-time responses that may be scaled up as time goes on, and have further modules added on to the present ones. Node. js services are becoming more popular, in order that they need one thing new all the time.