Power BI Training by Experts
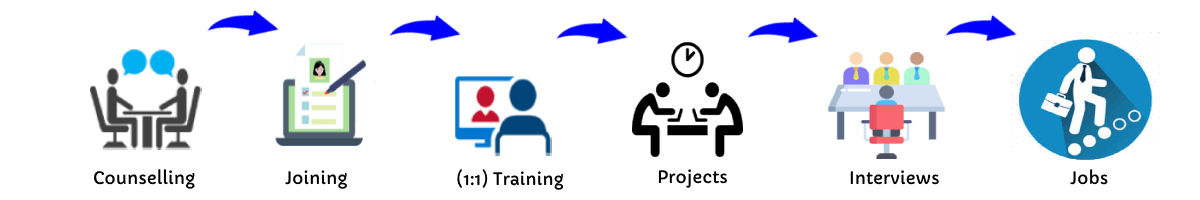
Our Training Process
Power BI - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Microsoft Power BI
Power BI Course Introduction
-
Welcome to Power BI
-
Business Intelligence and Data Analytics Overview
-
Introduction to Power BI
Installing Power BI
Power BI Course Introduction
- Welcome to Power BI
- Business Intelligence and Data Analytics Overview
- Introduction to Power BI
Installing Power BI
Design a Data Model
- Define the Tables
- Configure Table and Column Properties
- Define Date Table
- Develop a Data Model
- Apply Filtering
- Create Calculated Tables
- Create Calculated Columns
- Implement Row Level Security Roles
- Set up the Q and A Feature
- Optimize Model Performance
- Remove Unnecessary Rows and Columns
- Identify Poorly Performing Measures Relationships and Visuals
- Optimize Query Models
- Create and Manage Aggregations
- Report Generation
- Add Visualization Items to Report
- Choose an Appropriate Visualization Type
- Format and Configure Visualizations
- Apply Slicing and Filtering
- Create Dashboards
- Manage Tiles on a Dashboard
- Add a Dashboard Theme
- Use the Q and A Feature
Enhance Reports to Expose Insights
- Perform Top N Analysis
- Explore Statistical Summary
- Add a Quick Insight Result to a Report
- Use the Play Axis Feature of a Visualization
- Personalize Visuals
- Perform Advanced Analysis
- Identify Outliers
- Conduct Time Series Analysis
- Use Groupings
- Use the Key Influencers to Explore Dimensional Variances
- Manage Datasets
- Configure a Dataset Scheduled Refresh
- Configure Row level Security Group Membership
- Configure Incremental Refresh Settings
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 Power BI Mobile
Power BI Service: Power BI Service is cloud based Software as Service Application which allows us to create
dashboards, Setup schedule data refreshes, Share the reports securely in the organization. The Power BI Course Curriculum is designed via way of means of Microsoft Power BI Certified Experts. Power BI Desktop
2. Power BI Desktop: It is a Windows desktop application (Report Authoring Tool) which Lets you build queries,
models and reports that visualize data. We offer Microsoft Power BI industrial training in Toowoomba by Industry Experts. . Power BI Service
3. Power BI is the use of Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) programming language for enterprise analytics gear which connects to distinctive statistics reassets to research statistics and proportion insights for the duration of your organization. We provide Power BI internship in Toowoomba with live classes and courses. You can join Power BI Training in Toowoomba after attending our trail class by experts.
Power BI Mobile
Power BI Service: Power BI Service is cloud based Software as Service Application which allows us to create
dashboards, Setup schedule data refreshes, Share the reports securely in the organization. The Power BI Course Curriculum is designed via way of means of Microsoft Power BI Certified Experts. Power BI Desktop
2. Power BI Desktop: It is a Windows desktop application (Report Authoring Tool) which Lets you build queries,
models and reports that visualize data. We offer Microsoft Power BI industrial training in Toowoomba by Industry Experts. . Power BI Service
3. Power BI is the use of Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) programming language for enterprise analytics gear which connects to distinctive statistics reassets to research statistics and proportion insights for the duration of your organization. We provide Power BI internship in Toowoomba with live classes and courses. You can join Power BI Training in Toowoomba after attending our trail class by experts.