Vmware Training by Experts
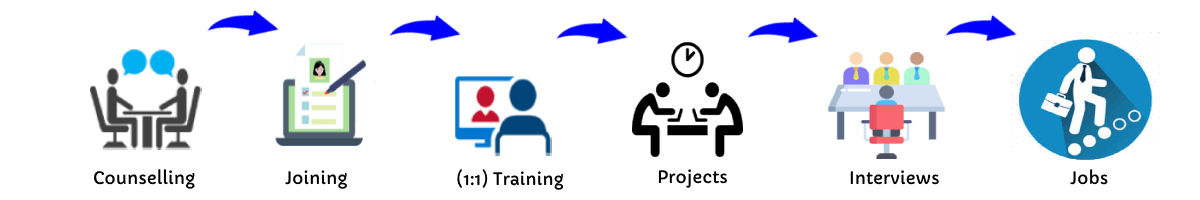
Our Training Process
Vmware - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Section 1 : Course Introduction
- Introductions and course logistics
- Course objectives
Section 2 : Introduction to VMware Virtualization
Section 3 : Configuring ESXi/ESX
Section 4 : Installing and Using VMware vCenter Server
Section 5: Networking
- Explain performance features of network adapters
- Explain the performance features of vSphere networking
- Use esxtop to monitor key network performance metrics
Section 6 : Storage Scalability
Section 7 : Virtual Machines
Section 8 : Access Control
Section 9 : Resource Monitoring
Section 10 : Scalability
Section 11 : High Availability and Data Protection
Section 12 : Configuration Management
- Patching using vCenter Update Manager
Section 13 : Installing ESX
- Discussion of virtualization & vSphere components /li>
- Configuration of ESXi and ESX
- Install and configure vCenterServer
- Use the VMware vSphere Client
- Configuration of vNetwork standard
- Distributed switches, network connections & port groups
- Storage management technologies
- Deploy virtual machines using templates
- VMware vCenter Converter
- Guided Consolidation
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates





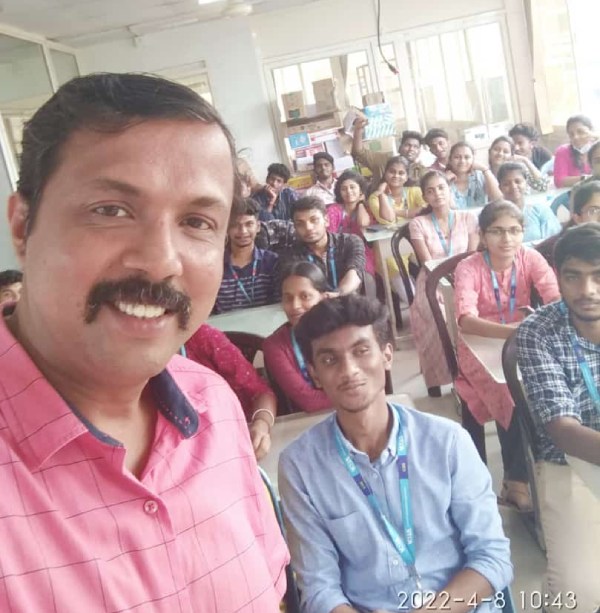
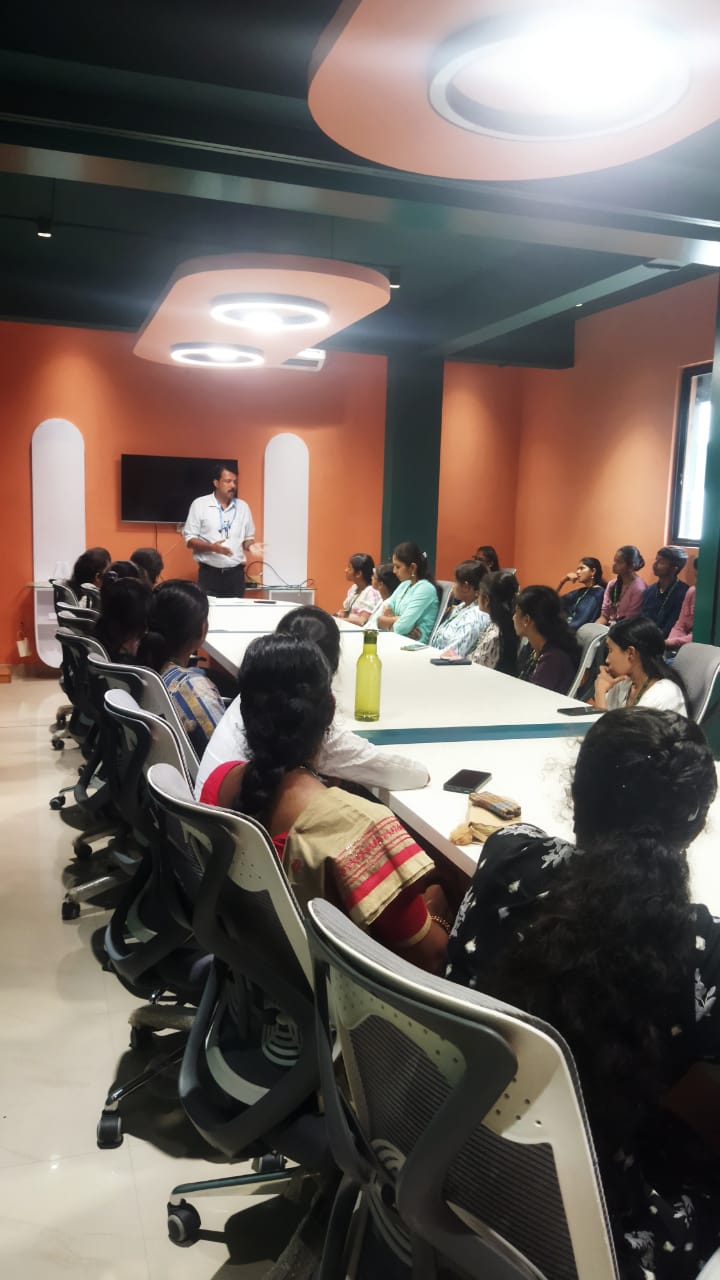
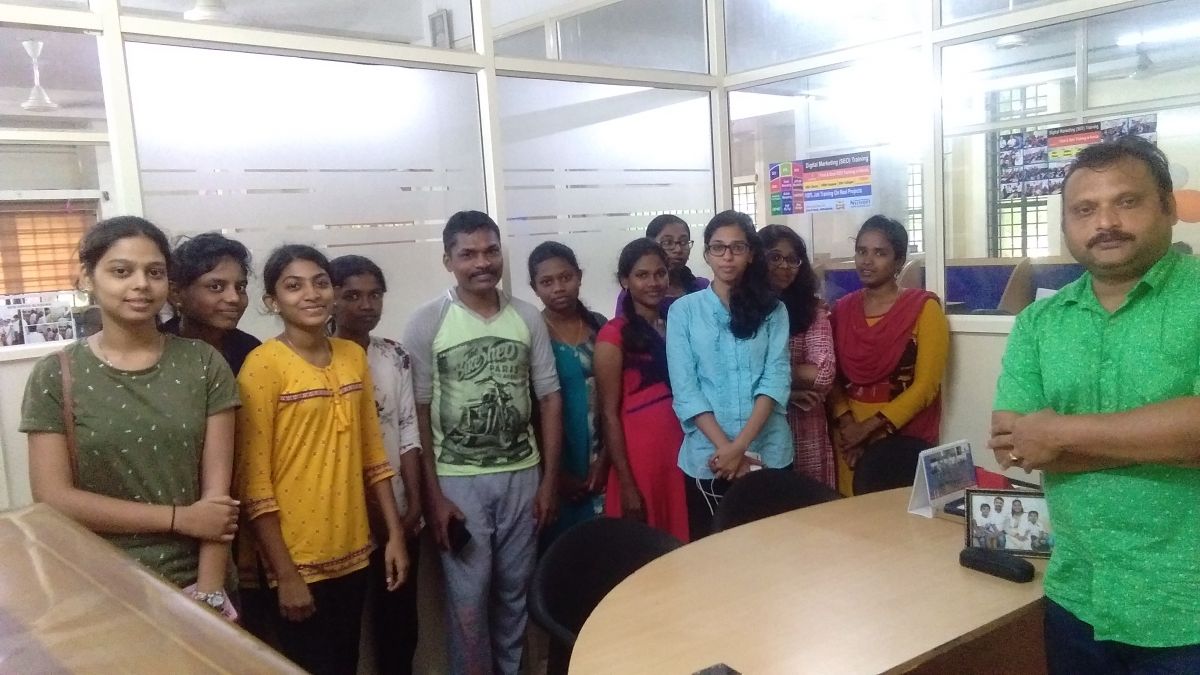
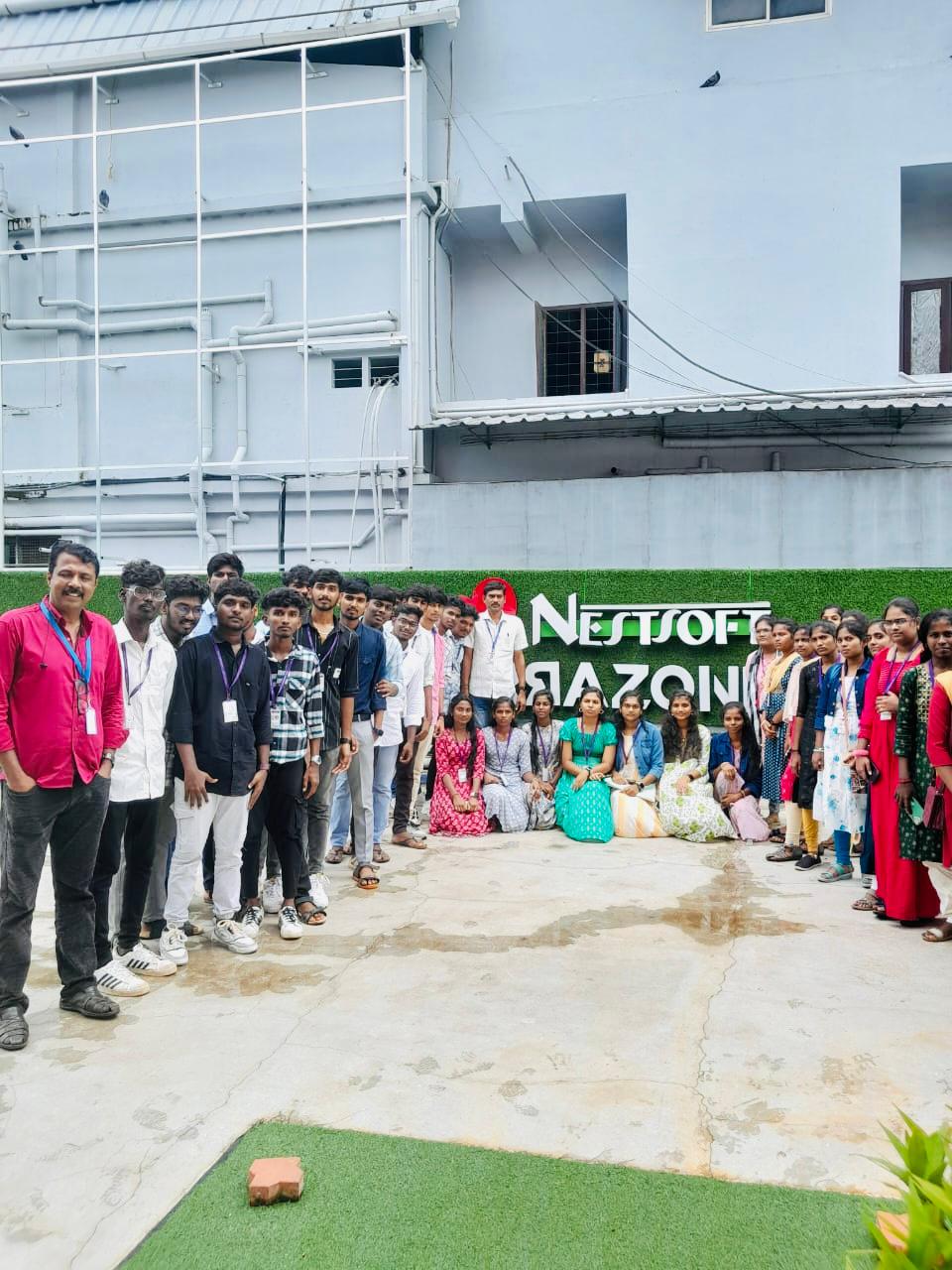
 Instructor-led or on-demand VMware training courses are frequently available to meet your preferred learning style. Virtualization is used by practically every industry now, and VMware Training in Toowoomba is in high demand. 0 as its basis. Students will be able to deploy VMware products and manage VMware cloud environments once they have completed training. To obtain a virtual understanding of the process, NESTSOFT's VMware training contains the important important theories of virtualization, such as Cloud Management and Automation, Data Center and Virtualization, Desktop and Mobility, and so on. Vmware Certified applicants get extensive understanding in Network Virtualization, Cloud Management, Digital Workspace, Data Center Virtualization, and other areas, and are able to work with any technology. You can take the exam to become a VMware certified professional after completing this course.
You will be acknowledged as a professional VMWare specialist after completing this course. Most IT and other businesses are now using VMWare as part of their IT infrastructure. Students receive hands-on training with VMware-certified equipment.
Instructor-led or on-demand VMware training courses are frequently available to meet your preferred learning style. Virtualization is used by practically every industry now, and VMware Training in Toowoomba is in high demand. 0 as its basis. Students will be able to deploy VMware products and manage VMware cloud environments once they have completed training. To obtain a virtual understanding of the process, NESTSOFT's VMware training contains the important important theories of virtualization, such as Cloud Management and Automation, Data Center and Virtualization, Desktop and Mobility, and so on. Vmware Certified applicants get extensive understanding in Network Virtualization, Cloud Management, Digital Workspace, Data Center Virtualization, and other areas, and are able to work with any technology. You can take the exam to become a VMware certified professional after completing this course.
You will be acknowledged as a professional VMWare specialist after completing this course. Most IT and other businesses are now using VMWare as part of their IT infrastructure. Students receive hands-on training with VMware-certified equipment.